Monitoring hosts traffic volume
The Hosts report shows the top hosts by data volume for the selected time period. For more information refer to Setting the time period for a report.
Traffic inbound into your LANLocal area network is reported separately from the outbound traffic. You can view internal and external hosts and data is graphed separately for Top Listeners and Top Talkers. This allows multi-site enterprises to monitor corporate systems while excluding Internet servers.
This report answers questions such as:
- What internal hosts are the top talkers and top listeners?
- Which external hosts are top talkers from which internal hosts are retrieving information?
- Which external hosts are top listeners from which internal hosts are sending information to?
- Could one host be choking out my network?
Use this information to determine if you need to create policies for these high data volume hosts. You may want to create protection policies for your business critical server machines or create control policies to limit hosts that are abusing the network.
VERSION INFO
The hosts report as a time-series is available in version 7.0.3 and higher.
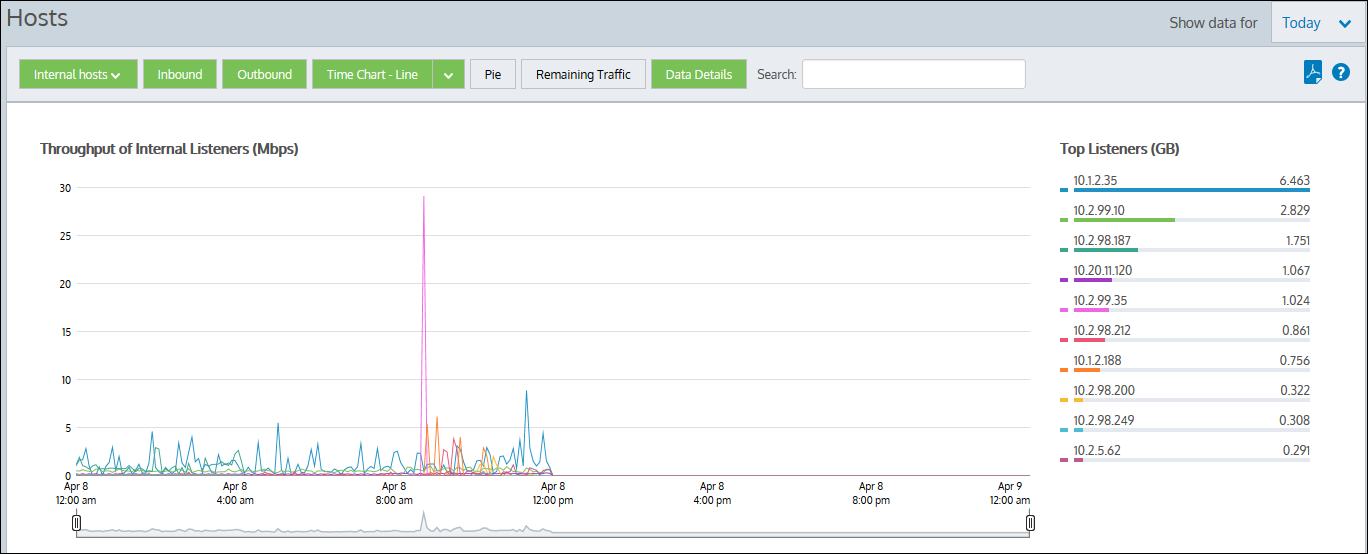
The Hosts report displays traffic volume over time and top listeners.
AVERAGE BANDWIDTH
Average bandwidth is calculated as the total bits observed in the charting interval divided by the number of seconds in that interval. E.g. For a chart with an hour of data, the intervals are five minutes.
Hosts are IPInternet protocol Address endpoint's in IP transactions and are usually client PCs or servers. During a flowthe network traffic between network objects, traffic flows from one host to another. Typically, one host is considered internal to your network; the other is external:
- Hosts that fall into a network objecta logical definition created and stored in the Exinda lilbrary, can represent any network component that was defined as internal are considered internal to your network
- Hosts that fall into a network object that was defined as external are considered external to your network
Traffic is inbound and outbound relative to your LAN – not relative to the host. Therefore, inbound traffic for an external host means that host was sending data inbound into your network.
To access the report:
- On your browser, open the Exinda Web UI (
https://Exinda_IP_address). - Key-in the User and Password.
- Click Login.
- Go to Monitor > Hosts.
Monitoring reports can be exported as a PDF document, saved as a scheduled report, or can be printed directly from the Web UI. For more information refer to Exporting, printing and scheduling reports.
Toggle various chart elements on and off by clicking the buttons above the charts. Note that when generating a PDF report of this screen, the toggle states are taken into account. That is, if you had toggled off the outbound charts, they will not be present in the PDF.
- Host Type: When you first load the Hosts report, Internal hosts are graphed by default. Click the Internal hosts button and then select External hosts to change the type. Note that you cannot graph both internal and external hosts at the same time.
- Traffic Type (Inbound/Outbound): By default, both Inbound and Outbound traffic is graphed. Click either the Inbound or Outbound option to hide the data. When viewing Internal hosts, hiding the Inbound data toggles off the Top Listeners data from the graphs, whereas hiding the Outbound data toggles off the Top Talkers data. When viewing External hosts, the opposite is true.
- Chart Type: The chart is initially mapped as a Stacked Area , but you can change the format to Line Chart if necessary.
- Pie: Toggles on or off a colour-coded Pie chart to the left of the Top Listeners and Top Talkers list.
- Remaining Traffic: Append or hide the Remaining Traffic data below the Top Listeners and Top Talkers lists. Reamining traffic represents the remaining application traffic on your network and the cumulative stack on the throughput chart represents all the hosts communicating through the appliance. If the remaining traffic show vastly more data volume than the top hosts, then the top hosts may look insignificant relative to the total, and so you may need to toggle off the remaining traffic category to see the relative differences and usage patterns of the top hosts.
NOTE
If there are more than 100,000 hosts to display, it may take several minutes to render the screen when Remaining Traffic is enabled.
- Data Details: Toggles on or off the data tables below the time series charts.
- Mouse Hover: Hover the mouse pointer over the graph to view data throughput at a given date and time. Refer to Chart Interactions - Drill in & Data brush in WUI Guided Tour for details.
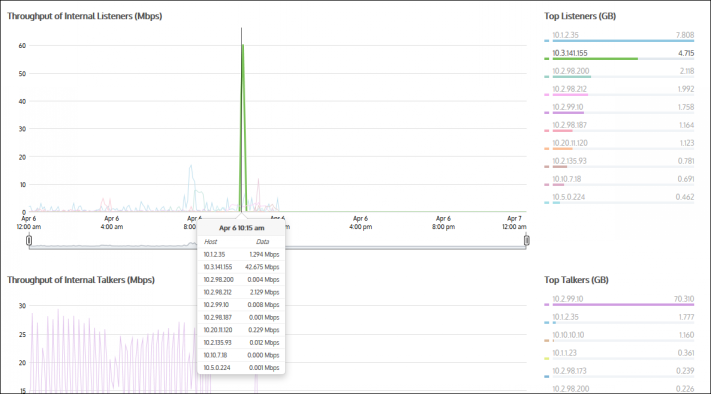
The Hosts report displays throughput by internal listeners over time broken down by top listeners and talkers.
Drill into the host data by clicking on a host in the Top Listeners or Top Talkers list (located to the right of the graphs). Click a particular host to view the Applications Report for the host that you selected. You can then use the selector on the Applications Report page to show URLs or conversations that involved the host.
The tables at the bottom of the Hosts report information for the top listeners and talkers and include the IP Address, the Total Volume of data, and the Average Throughput rates. Click on any entry in the table to open the Applications Report for that specific host.
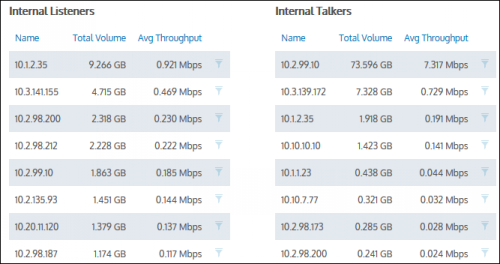
Drilling down into hosts data.
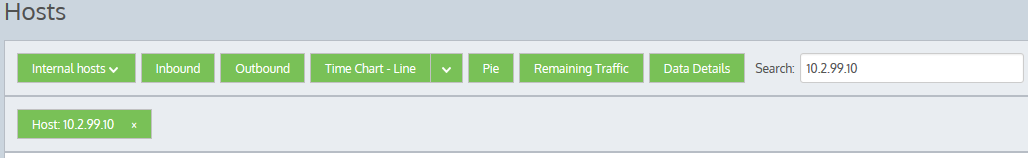
If the host you are looking for is not listed in the Top hosts, you can use the search function to locate data for a single host only. Type a single IP Address in the Search field to locate data for a particular host. If entering an IPv6 host, use the full IPv6 address only. When the data is retrieved, the individual host is shown on the filter bar below the button bar. To turn off the filtering, click on the close 'x' in the filter tag.
- To understand how to set the desired time range for a chart, see Setting the Time Range.
- To understand how to the charts interact and what the toggle buttons do, see Understanding How Charts Relate.
- To understand how to drill into the data to find particular filtered data, see Drilling into the Data.
- To understand the difference between inbound and outbound traffic, see Understanding Traffic Direction.
- To understand how many data points are shown for each time period, see Understanding Traffic Granularity.
- To understand how to print the report or schedule the report, see Printing and Scheduling Reports.