Monitoring subnets
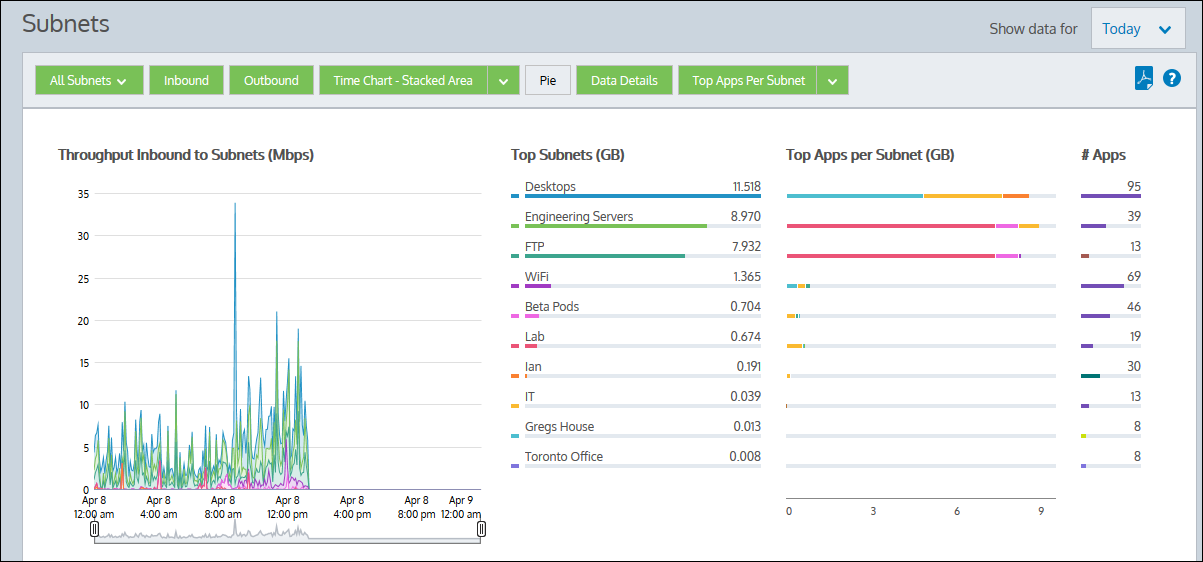
A subnet, a type of network objecta logical definition created and stored in the Exinda lilbrary, can represent any network component, can include multiple network subnets and/or multiple IPInternet protocol addresses. The Subnets report shows the top subnets by volume and their average throughput for the selected time period.
When subnets are defined, they can be specified as internal or external to your network. Inbound and outbound traffic for these subnets are reported separately. Inbound and outbound traffic is relative to the subnet, not relative to the Exinda Appliance.
Subnets are not required to be mutually exclusive. Traffic may be reported in more than one subnet. You can optionally show the top three applications for each of the top subnets.
These charts can answer questions such as:
- What are the top subnets in my network?
- How much bandwidth does my subnet for the New York branch or for my finance department or for my PBX phones typically consume?
- Do each of my branches or departments (partitioned by subnet) have the same top applications?
Toggle chart components on and off by clicking the buttons at the top of he report. Note when generating a PDF report of this screen, toggle states are taken into account.
NOTE
Average bandwidth is calculated as the total bits observed in the charting interval divided by the number of seconds in that interval. E.g. For a chart with an hour of data, the intervals are five minutes.
Once Network Objects get modified, it can lead to some discrepancies on how Exinda Appliance shows data in the Subnet report. Some sections of the reports may become out of sync when drilling down into conversations, URLs, and hosts. It may happen because the report shows data for all the subnets, including the ones defined before and after the change. Which subnets are included in the reports depends on the covered time period and when exactly the change happened. On the other hand, the drilled-down sections always show data based on the newer subnet definitions. Thus, it will include only data collected after the modifications.
The Subnet report has a granularity of five minutes, but for some technical limitations, the drilled-down records have a lower granularity of one hour. It leads the drilled-down records to show different data for the selected period.
To access the report:
- On your browser, open the Exinda Web UI (
https://Exinda_IP_address). - Key-in the User and Password.
- Click Login.
- Go to Monitor > Subnets.
Monitoring reports can be exported as a PDF document, saved as a scheduled report, or can be printed directly from the Web UI. For more information refer to Exporting, printing and scheduling reports.
Create a network object. See For more information refer to Adding network objects ..
If Network Object/Subnet statistics collection is disabled, the Subnets report will not include application data for the time period the collection was disabled. For more information refer to Adding network objects .
If the Subnet Report checkbox is not enabled on the definition of the subnet, then the data will not be included in the report. If the data was collected, then enabling the Subnet Report will immediately show the data in the chart.
Press the down arrow next to the Stacked Chart button to select Line Chart to switch to the line chart. Conversely, press the down arrow next to the Line Chart button to select Stacked Chart and switch to the stacked area chart. The line chart shows the subnets against the common zero baselineused by monitors and performance reports to establish a standard by which sunsequent performance can be measured so that the throughput of the subnets can be compared with one another and the pattern of a specific subnet is clearer. You can look for particular patterns such as spikes or flat tops. If your subnets are not defined to be mutually exclusive, displaying the throughput in a line chart with a common zero baseline may make the most sense, as the cumulative values chart will double count some data and may not be meaningful. However, if you have defined your subnets to be mutually exclusive then stacked area charts is an option.
Toggle on the pie chart by clicking the Pie button. Note that if your subnets are not defined to be mutually exclusive, that is, data is captured in more than one subnet, then the pie chart does not hold much meaning.
The number of subnets shown are configurable. Note that this configuration applies to all charts on the appliance. For more information refer to Monitoring Configuration.
In general, yes. However, there are some cases where the traffic direction is different for subnets versus virtual circuits and so the totals will not match. For more information refer to Determining traffic direction and the implications of directional flow on reports.
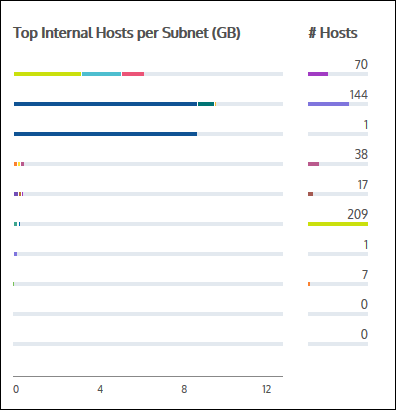
By default, this report displays the Top Apps per subnet, but you can change the view to Top Internal or Top External Hosts per Subnet. Click the drop-down arrow beside the Top Apps per Subnet button to view these other options. When the display updates, the Top hosts data is mapped to a bar graph. You can brush over any host to view it's IP Address and throughput data.
NOTE
Toggling the Top Internal Hosts per Subnet and Top External Hosts Per Subnet within this report is available in version 7.0.3 and higher.
You can drill into the applications for a specific subnet by clicking on the subnet name in the Top Subnets chart or by clicking on the subnet name in the table below the charts. You can also drill into the hosts, or users, or conversations for a particular subnet by clicking on the View Users, View Conversations, View URLs links in the table. The applications, hosts, users, conversations, or URLs graph will be shown filtered for the specified subnet.
- To understand how to set the desired time range for a chart, see Setting the Time Range.
- To understand how to the charts interact and what the toggle buttons do, see Understanding How Charts Relate.
- To understand how to drill into the data to find particular filtered data, see Drilling into the Data.
- To understand the difference between inbound and outbound traffic, see Understanding Traffic Direction.
- To understand how many data points are shown for each time period, see Understanding Traffic Granularity.
- To understand how to print the report or schedule the report, see Printing and Scheduling Reports.