Detecting that Kerio Connect has been compromised and used for spamming
Your server may be compromised if any of the following happens:
- Your Kerio Connect server is slow.
- Users get bounce backs of emails they did not send.
- Your Kerio Connect server IP addressAn identifier assigned to devices connected to a TCP/IP network. (external IP) is getting blacklisted.
- A large email queue consists of multiple email messages sent to addresses that you do not normally sent to. These messages maybe send to Yahoo, AOL, Hotmail, and so on.
A combination of the above may point that someone’s password being guessed, or a user’s machine has received a virus/Trojan that is mass emailing/spamming.
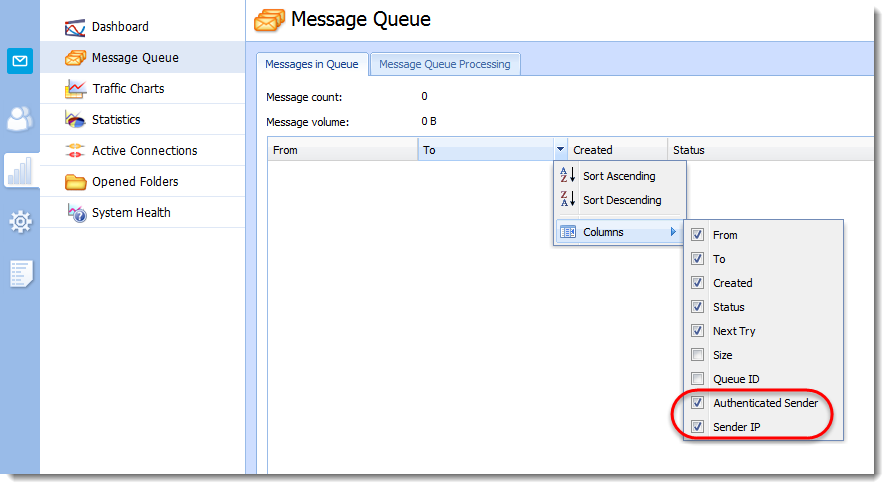
Verifying message senders in the message queue
Kerio Connect can display information on who sends messages and where these messages come from.
- In the administration interface, go to Status > Message Queue.
- Right-click any column header.
- Click Columns.
- Select Authenticated Sender and Sender IP.
Authenticated sender can indicate that user's password may have been compromised.
Sender IP can help to indicate if the email are sent internally (this can point to a virus or a Trojan on a local user machine), or external (this can point to a guessed password of an authenticated user).
Example
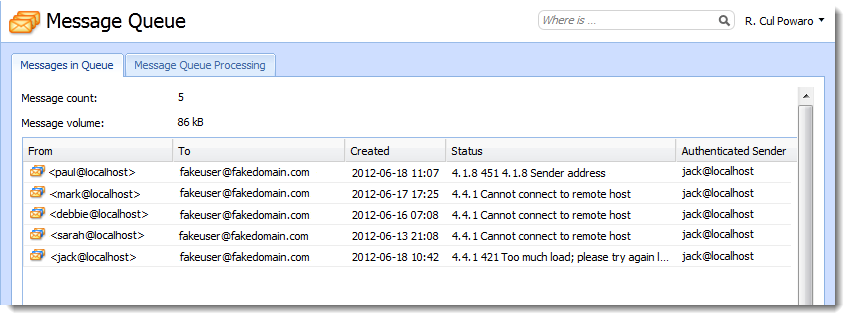
In the example above:
- The From address is constantly changing and sending to
fakedomain.com. - The Authenticated Sender is always
jack@localhost. This could indicate that Jack’s password has been compromised/guessed.
To correct this issue:
- Change the user's password. As a precaution, change passwords of all users. For information about creating strong passwords, see Password policy in Kerio Connect
- Run a virus/malware scan on any machine that the user has used. This should detect any possible compromise and stop spam emails form being sent via your server.