In-path topologies
Exinda Appliances are often deployed between a core switch and a WANWide Area Network/Internet router. In this type of deployment, the Exinda Appliance is referred to as inlineIn network terminology, an inline device receives packets and forwards them to their intended destination. Routers, firewalls and switches are examples of inline devices. The inline designation also alerts you the device is critical to network function. If the device goes down, network traffic is affected., which is a way to describe a network device in a primary network path that receives packets and forwards them to their destinations. In this case, the Exinda Appliance receives packets from the core switch and sends them to the Internet/WAN router and vice versa.
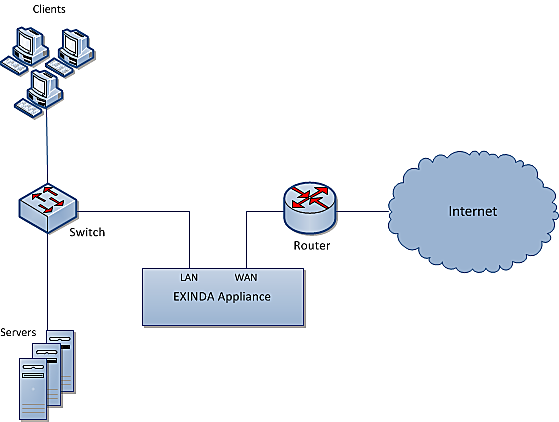
Inline deployment of an Exinda Appliance
Usually, the WAN port on your Exinda appliance is cabled to the WAN/Internet router, using the crossover Ethernet cable. And the LANLocal area network port on your Exinda appliance is cabled to the core switch, using the straight Ethernet cable. If your appliance has a dedicated management port, it also needs to be cabled to an internal switch using an Ethernet cable. Both cables are shipped along with the appliance.
For more information refer to Basic characteristics and behaviors of Exinda Appliances.
For specific information about your model, download its Quick Start Guide.
Once all Ethernet cables are in place, power the Exinda Appliance off and ensure the network connectivity. Then, power on the Exinda Appliance, let it fully boot and ensure network connectivity.
The following topics describe how to configure and operate your Exinda Appliance within various in-pathIn-path refers to placing an between network devices that send and receive data packets to each other, like a switch and a router. An appliance deployed in-path automatically inspects all packets traveling along the path. topologies.