Collecting SNMP Traps Messages
SNMP is a data logging service that enables networked devices to log events and information through data messages (technically known as SNMP TrapsNotifications/alerts generated and transmitted by active network components (Example: hubs, routers and bridges) to SNMP server(s) whenever important events such as faults or security violations occur. Data contained in SNMP Traps may contain configuration, status as well as statistical information such as number of device failures to date.). SNMP messaging technology is similar in concept to Syslogs - where unlike Windows® and Text logs based environments, devices that generate SNMP messages do not record events data in local logs. Instead events information is sent in the form of data messages to an SNMP Trap Server which manages and saves SNMP message data in a local (centralized) log file.
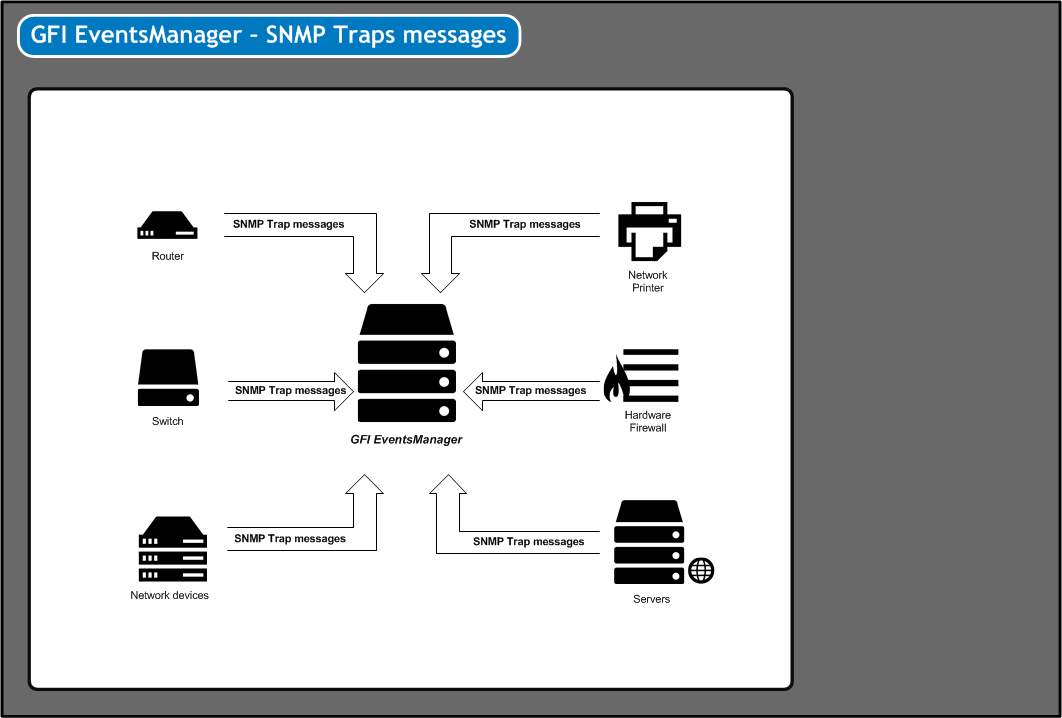
SNMP Trap messages must be directed to the computer running GFI EventsManager
Note
GFI EventsManager natively supports an extensive list of SNMP devices and Management Information Bases (MIBs). For a full list of supported devices, view the following KBASE article: http://go.gfi.com/?pageid=esm_syslog_snmp_support
GFI EventsManager includes a dedicated SNMP Trap Server through which SNMP Traps are handled. A built-in buffer allows the SNMP Trap Server to collect, queue and forward up to 30 SNMP Trap at a time. Buffered logs are by default passed on to the event processing engine as soon as the buffer fills up or at one minute intervals; whichever comes first.
Important
Before you start collecting SNMP Traps messages, every SNMP event source (workstations, servers and/or network devices) must be configured to send their SNMP Traps Messages to the computer name or IP where GFI EventsManager is installed.
To collect SNMP Traps:
1. From Configuration tab > Event Sources, right-click an event source or group and select Properties.
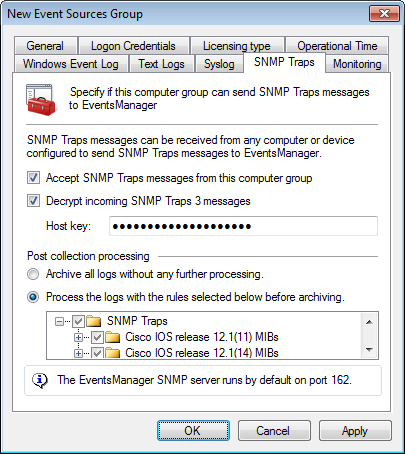
Collecting SNMP Traps
2. Click SNMP Traps tab and select Accept SNMP Traps messages from this event source to enable the collection of SNMP Traps.
3. Select Decrypt incoming SNMP Traps 3 messages and specify the security key in the Host key text box.
4. Select ArchiveA collection of events stored in the SQL Server based database backed of GFI EventsManager. events in database to archive collected events without applying events processing rules.
5. Select Process using these rule sets and select the rule sets you want to run against the collected events.
6. Click Apply and OK.
Note
The GFI EventsManager SNMP Trap Server is by default configured to listen for SNMP Trap messages on port 162. For more information refer to Configuring the SNMP Traps server.
Note
The built in SNMP Trap Server supports SNMP version 3 Traps with encryption. For encrypted SNMP messages the encryption host key must be provided in the decrypt incoming SNMP Traps 3 message field.
Important
Deleting event logs without archiving may lead to legal compliance penalties.
Configuring the SNMP Trap server
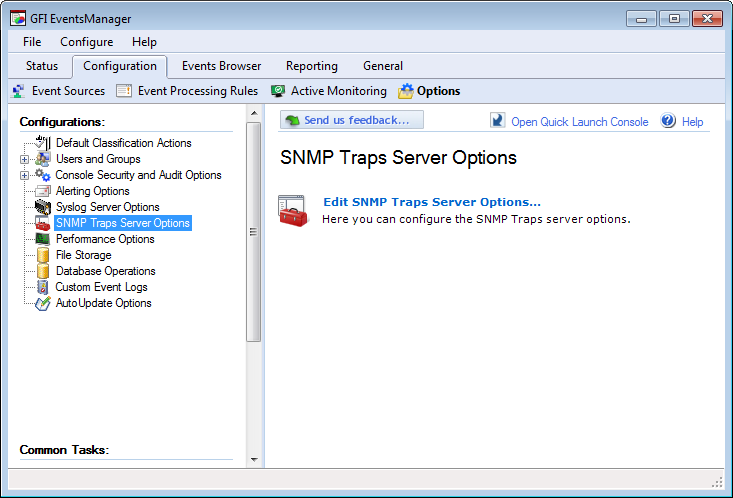
Configuring SNMP Traps
To change the default SNMP Trap Server settings:
1. Click Configuration tab > Options.
2. Right-click SNMP Traps Options and select Edit SNMP Traps options…
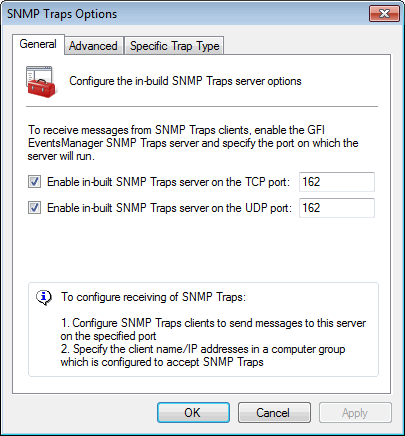
SNMP Traps options
3. Enable the required TCP/UDP SNMP server. Specify the TCP/UDP port on which GFI EventsManager will listen for SNMP messages.
4. Click Advanced tab to add, edit or remove SNMP Trap object identifiers (OIDs).
5. Click Specific Trap Type tab to add, edit or remove trap types.
6. Click Apply and OK.
Note
When configuring SNMP Trap Server port settings, make sure that the configured TCP or UDP port is not already in use by other installed applications. This may affect the delivery of SNMP Trap messages to GFI EventsManager.