Interpreting scan results
The Scan Results Overview and Scan Results Details sections in the Scan tab, are designed to facilitate the result analysis process as much as possible. Use the information in the following sections to learn how scan results are interpreted and to know which areas require your immediate attention:
 Viewing scan results
Viewing scan results
Use this section to interpret results generated by manual scans and results stored in the database backend. For more information refer to Manual scans.
To view scan results:
- Launch GFI LanGuard and click the Scan tab.
- Launch a new scan or load the result from the database/file. For more information refer to Loading results from the database.
- Once completed, the results are displayed in the Scan Result Overview and the Scan Results Details sections.
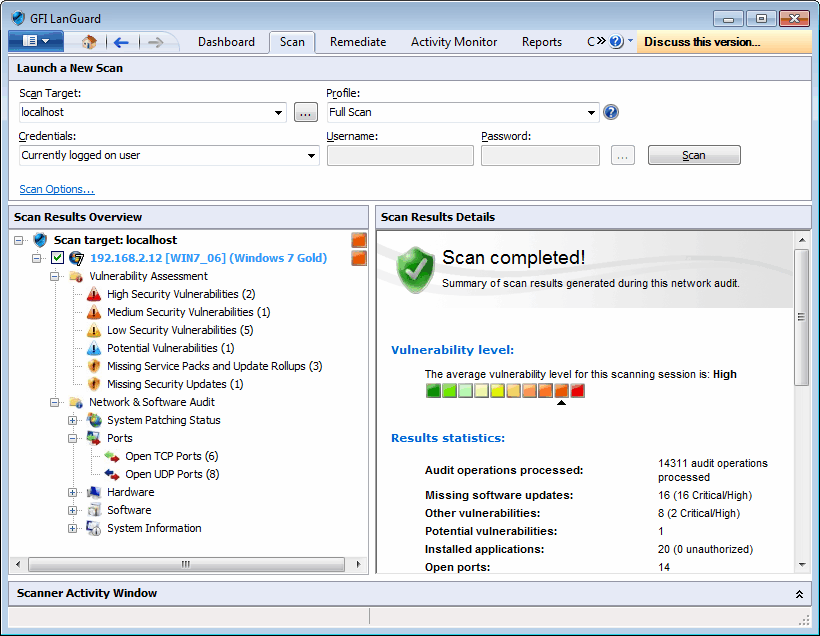
Results overview
From Scan Results Overview, expand a computer node to access results retrieved during the scan. Security scan results are organized in two sub–nodes tagged as:
While a scan is in progress, each computer node has an icon that categorizes the response time. The table below describes the different icons used by GFI LanGuard to categorize the response time. The first icon indicates that the scan is queued, while the second icon indicates that the scan is in progress.
| Category | Information | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Fast response | Less than 25ms |
|
Medium response | Between 25ms and 100ms |

|
Slow response | More than 100ms |
 Vulnerability Level Rating
Vulnerability Level Rating
The GFI LanGuard vulnerability level is a rating assigned to each scanned computer. The rating can be viewed from:
- Scan Results Details – This section in the Scan tab provides you with a vulnerability level meter assigned the computers/groups that have been scanned
- DashboardA graphical representation that indicates the status of various operations that might be currently active, or that are scheduled. – The Dashboard section provides you with information for specific computers or selected groups of computers, from the computer tree. Select the computer/group and view the vulnerability meter from the right pane. Select Entire Network to view the vulnerability level for all your scan targets.

Vulnerability level meter
How is the vulnerability level calculated?
The vulnerability level is calculated using a weighting system. After a scan, GFI LanGuard groups the discovered vulnerabilities in categories sorted by severity rating:
- High
- Medium
- Low
For each rating, a weighted score is given. This is based on the total number of vulnerabilities per category.
NOTE
When the vulnerability level cannot be assessed or vulnerability scanning was not performed, GFI LanGuard gives a rating of N/A.
Weight scores
| Category | Number of Detected Vulnerabilities | Scores |
|---|---|---|
| High Vulnerabilities |
1-2 3-5 > 5 |
8 9 10 |
| Medium Vulnerabilities |
1-2 3-5 > 5 |
5 6 7 |
| Low Vulnerabilities |
1-2 3-5 > 5 |
2 3 4 |
Score classification
After categorizing detected vulnerabilities and generating a score for each category, the overall vulnerability level is generated. The vulnerability level is the severity rating with the highest score.
Vulnerability level scores:
- A score of >= 8, results in High vulnerability rating
- A score of <= 7 and >= 5, results in Medium vulnerability rating
- A score of <= 4 and >=1, results in a Low vulnerability rating
Example
During a scan of Computer A, the following vulnerabilities were discovered:
- 3 high vulnerabilities
- 8 medium vulnerabilities
- 5 low vulnerabilities
The score for each category was calculated with the following results:
- 3 high vulnerabilities = 9
- 8 medium vulnerabilities = 7
- 5 low vulnerabilities = 3
The vulnerability level for Computer A is therefore HIGH.
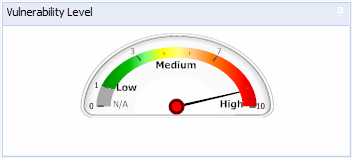
Dashboard Vulnerability Meter
The vulnerability level is indicated using color–coded graphical bar:
- Red bar = high vulnerability level
- Green bar = low vulnerability level.
 Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability Assessment
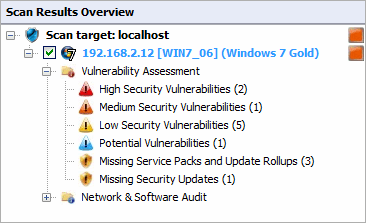
The Vulnerability Assessment node
Click on any Vulnerability Assessment node to view the security vulnerabilities identified on the target computer grouped by type and severity.
High Security Vulnerabilities
Click on the High Security Vulnerabilities or Low Security Vulnerabilities sub–nodes for a list of weaknesses discovered while auditing a target device. Groups are described in the following table:
| Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Mail, FTPA protocol used to transfer files between network computers., RPC, DNSA database used by TCP/IP networks that enables the translation of hostnames into IP numbers and to provide other domain related information. and Miscellaneous | Shows vulnerabilities discovered on FTP servers, DNS servers, and SMTP/POP3/IMAP mail servers. Links to Microsoft® Knowledge Base articles or other support documentation are provided. |
| Web | Lists discovered vulnerabilities on web servers (such as wrong configuration issues). Supported web servers include Apache, Internet Information Services (IIS®) and NetscapeA web browser originally developed by Netscape Communications Corporation.. |
| Services | Lists vulnerabilities discovered in active services as well as the list of unused accounts that are still active and accessible on scanned targets. |
| Registry | Registry settings of a scanned network device are listed. Links to support documentation and short vulnerability descriptions are provided. |
| Software | Enumerates software installed on the scanned network device(s). Links to supporting documentation and short vulnerability descriptions are provided. |
| Rootkit | Enumerates discovered vulnerabilities because of having a rootkit installed on the scanned network device(s). Links to supporting documentation and short vulnerability descriptions are provided. |
Potential vulnerabilities
Select Potential vulnerabilities sub–node to view scan result items classified as possible network weaknesses. Although not classified as vulnerabilities, these scan result entries still require particular attention since malicious users can exploit them during malicious activity.
For example, during vulnerability scanning GFI LanGuard enumerates all modems installed and configured on target computers. If unused, modems are no threat to your network. If connected to a telephone line these modems can, however, be used to gain unauthorized and unmonitored access to the Internet. Users can potentially bypass corporate perimeter security including firewalls, antivirus, website rating and web content blocking. This exposes the corporate IT infrastructure to a wide range of threats including hacker attacks. GFI LanGuard considers installed modems as possible threats and enumerates them in the Potential Vulnerabilities sub–node.
Missing Service Packs
Click Missing Service Packs and Update Rollups or Missing Security Updates sub–nodes to check any missing software updates or patches. For a full list of missing service packs and missing patches that can be identified by GFI LanGuard, refer to http://go.gfi.com/?pageid=ms_app_fullreport
Bulletin information.
To access bulletin information, right–click on the respective service pack and select More details>Bulletin Info.
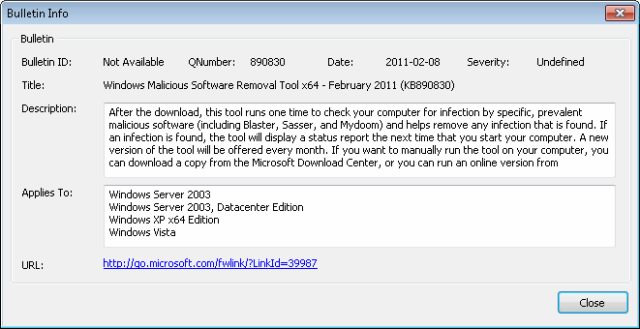
Bulletin info dialog
 Network & Software Audit
Network & Software Audit
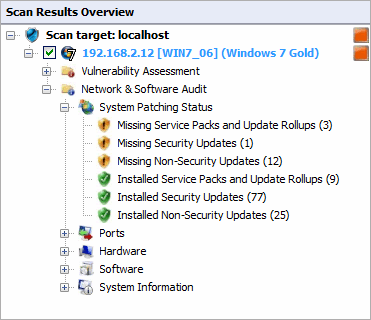
The network and software audit node
Click Network & Software Audit to view security vulnerabilities identified on scanned targets. In this section, vulnerabilities are grouped by type and severity.
Click System Patching Status to view all missing and installed patches on a target machine. Available links are:
- Missing Service Packs and Update Rollups
- Missing Security Updates
- Missing Non-Security Updates
- Installed Service Packs and Update Rollups
- Installed Security Updates
- Installed Non-Security Updates.
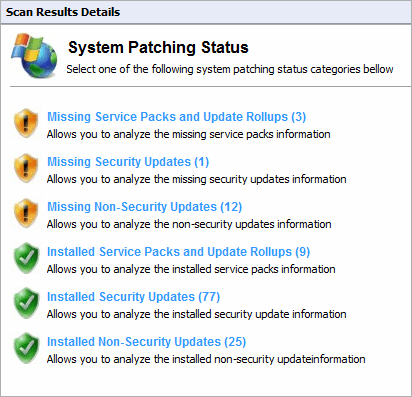
System patches status
Click Ports to view all open TCP and UDP portsAn acronym for User Datagram Protocol, these used to transfer UDP data between devices. In this protocol received packets are not acknowledged. detected during a scan. If a commonly exploited port is discovered to be open, GFI LanGuard marks it in red.
NOTE
Some software products may use the same ports as known TrojansA form of malware that contains a hidden application that will harm a computer.. For additional security, GFI LanGuard identifies these ports as a threat.
Apart from detecting open ports, GFI LanGuard uses service fingerprint technology to analyze the services that are running behind the detected open ports. With service fingerprint, GFI LanGuard can detect if malicious software is using the detected open port.
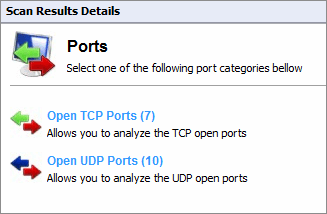
All UDP and TCP portsAcronym for Transmitting Control Protocol. This protocol is developed to allow applications to transmit and receive data over the internet using the well-known computer ports., found during a scan
Click Hardware to view all details discovered by the hardware audit. The hardware audit, amongst others, displays information such as MAC addresses, IP addresses, device type; device vendor etc. The table below describes the hardware information groups:
Click Software to view all details involved in the software audit. The software audit amongst others displays information such as:
- Application name
- Publisher
- Version.
The table below describes the hardware information groups:
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
| General Applications | Enumerates installed software on scan targets. |
| AntivirusA software countermeasure that detects malware installed on a computer without the user's knowledge. Applications | Lists installed antivirus engines on scan targets. |
| Instant Messenger Applications | Lists all detected instances of Instant messenger applications on scan targets. |
| Patch Management Applications | Lists all the installed patch management applications, detected on your scan targets during a scan. |
| Web Browser Applications | Contains scanned targets that have Internet browsers installed. |
| Firewall Applications | Enumerates information on installed Firewall applications on scan targets. |
| Antiphishing Applications | Lists information of installed antiphishing engines on scan targets. |
| VPN Client Applications | Includes information on installed Virtual Private Network clients on scan targets. |
| Peer–To–Peer Applications | Shows installed Peer–To–Peer applications on scan targets. |
Click System Information to view all details related to the operating system installed on a target machine. Table below describes the system information groups:
| Category | Information | Identify |
|---|---|---|
| Shares |
|
|
| Password Policy |
|
|
| Security Audit Policy |
|
NOTE To view Security Audit Policy, enable auditing on target computers. For more information refer to Enabling security audit policies. |
| Registry |
|
|
| NETBIOSAn acronym for Network Basic Input/output. This system provides services to allow applications on different computers within a network to communicate with each other. Names |
|
|
| Groups |
|
|
| Users |
|
|
| Logged On Users |
|
|
| Sessions |
|
|
| Services |
|
|
| Processes |
|
|
| Remote TOD (time of day) |
|
|