Deployment scenarios
GFI LanGuard deployments depend on the number of computers and devices you want to monitor and traffic load on your network during normal operation time. Refer to the following deployment scenarios to determine whether you want to:
Any GFI LanGuard deployment starts with installing the product in your environment. After a GFI LanGuard instance is successfully installed, it will:
- Determine reachable machines on your network and collect information from target machines as part of its Network Discovery operations, using a subset of SMB, NETBIOSAn acronym for Network Basic Input/output. This system provides services to allow applications on different computers within a network to communicate with each other., and ICMP protocols. Supported targets include the localhost, IP, computer name, computers list, IP range, whole domain/workgroup and/or organizational unit.
- Once targets are identified, GFI LanGuard performs a scan to enumerate all the information related to the target computer. GFI LanGuard uses a variety of techniques to gain access to this information ranging from file and folder property checks, registry checks, WMI commands, SMB commands as well as port scan checks (TCP/UDP) and more.
With GFI LanGuard Central Management Server, multiple GFI LanGuard instances can be brought together through a common console, even when installed in separate locations. The GFI LanGuard Central Management Server console offers administrators a view of the security and vulnerability status for all computers, networks or domains managed by the different GFI LanGuard instances. It also offers centralized reporting and visibility by capturing data from the various deployments of GFI LanGuard. For more information refer to GFI LanGuard Central Management Server.
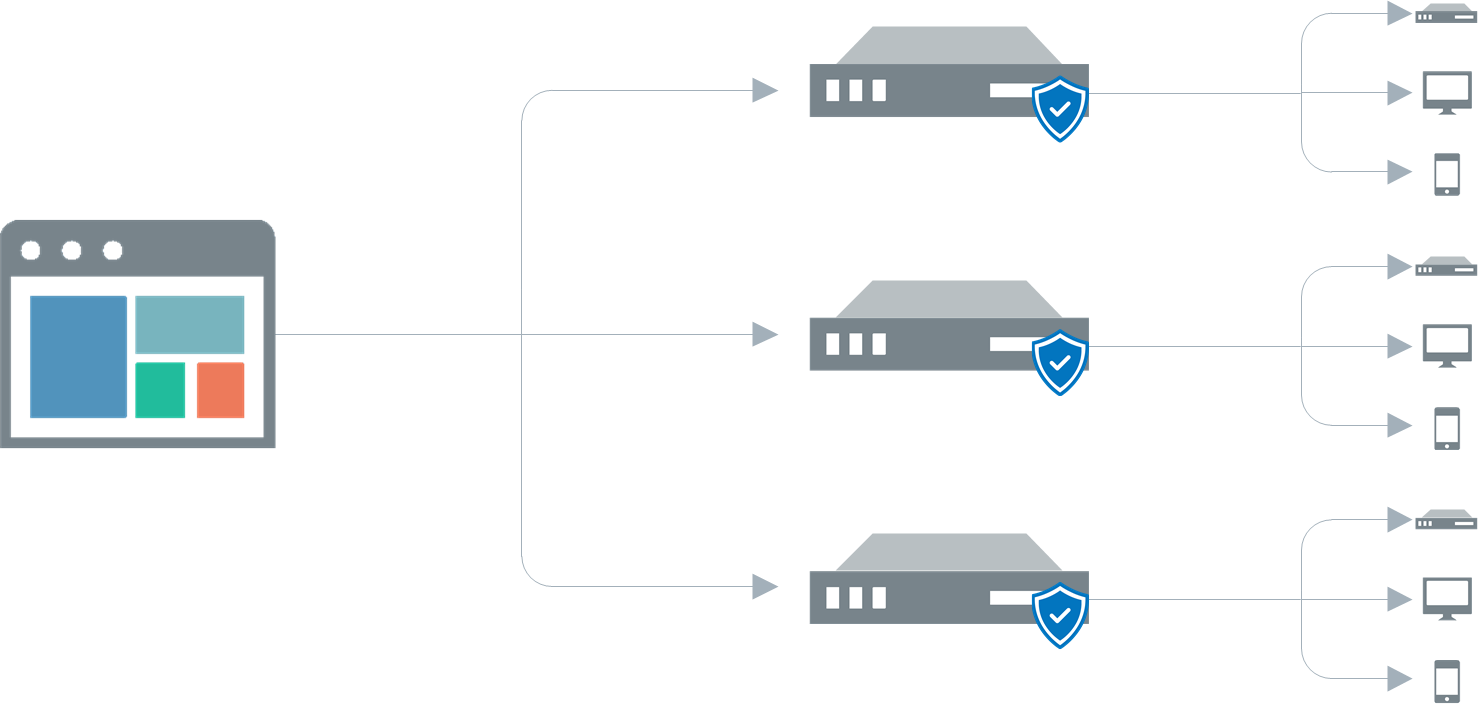
GFI LanGuard Central Management Server is used only for reporting. Scans and remediation take place only in GFI LanGuard and then information is centralized to GFI LanGuard Central Management Server soon after it becomes available in GFI LanGuard. Synchronization usually takes a few minutes. Delay depends on network size and amount of data being transferred.
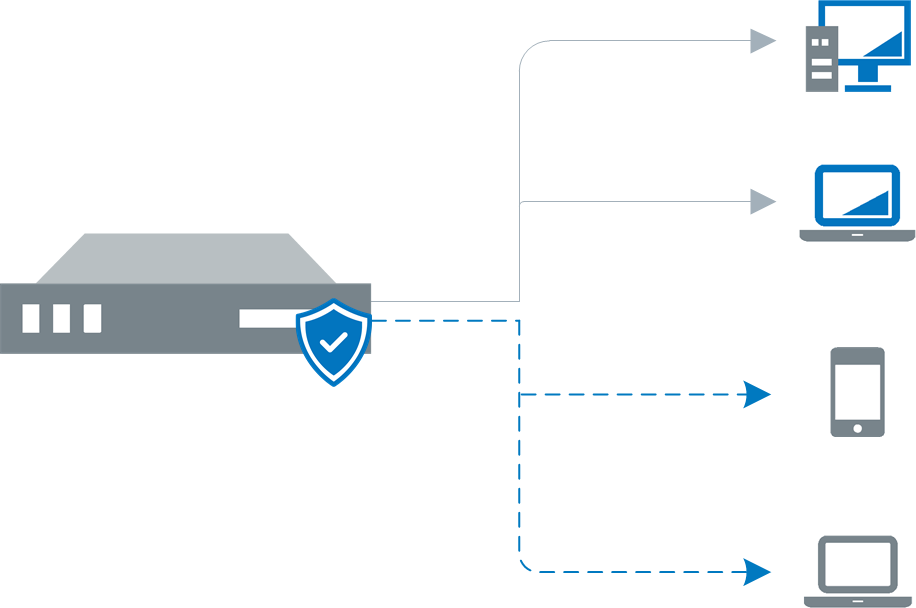
Agent-less auditing is started from GFI LanGuard. GFI LanGuard creates a remote session with the specified scan targets and audits them over the network. On completion, the results are imported into the results database and the remote session ends. You can audit single computers, a range of specific computers and an entire domain/workgroup. For more information refer to Manual scans.
NOTE
Scans in Agent-less mode use the resources of the machine where GFI LanGuard is installed and utilize more network bandwidth since auditing is done remotely. When you have a large network of scan targets, this mode can drastically decrease GFI LanGuard's performance and affects network speed. In larger networks, deploy Agents/Relay Agents to balance the load appropriately.
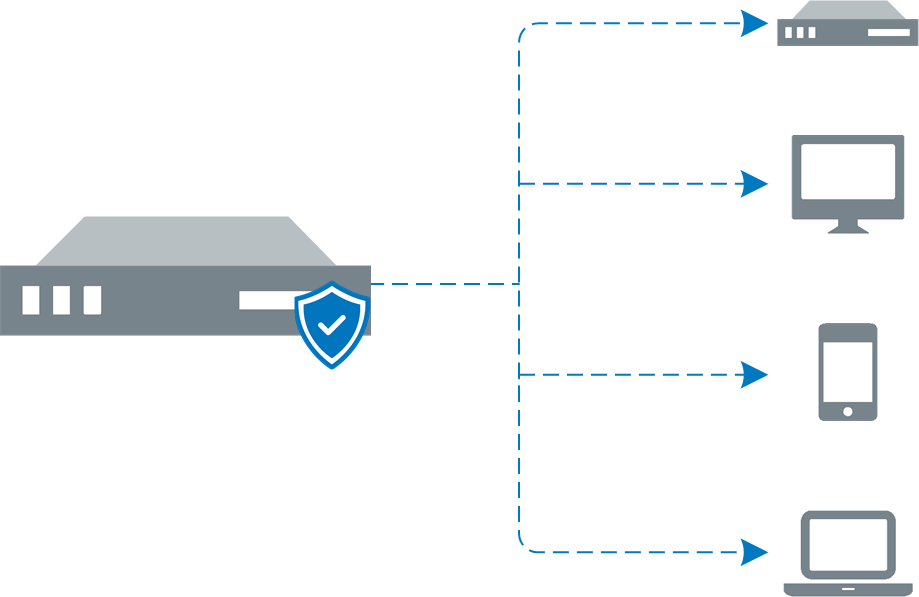
GFI LanGuard can be configured to automatically deploy agents on newly discovered computers. Agents minimize network bandwidth utilization. This is because in Agent-less mode, the GFI LanGuard server component performs audits over the network; while in Agent mode, audits are done using the scan target's resources and only a result XMLAn open text standard used to define data formats. GFI LanGuard uses this standard to import or export scanned saved results and configuration. file is transferred over the network.

Agents send scan data to GFI LanGuard through TCP port 1072. This port is opened by default when installing GFI LanGuard. Agents do not consume resources of the scan target's machine unless it is performing a scan or remediation operations. If an Agent becomes unresponsive for 60 days, it is automatically uninstalled from the target machine. For more information refer to Managing Agents.
NOTE
GFI LanGuard Agents can be deployed only on machines running Microsoft Windows operating systems that meet a minimum set of system requirements. For more information refer to GFI LanGuard system requirements.
Relay agents are used to reduce the load from the GFI LanGuard server. Computers configured as relay agents download patches and definitions directly from the GFI LanGuard server and forward them to client computers. The main advantages of using relay agents are:
- Save Network Bandwidth in local or geographically distributed networks. If a relay agent is configured on each site, a patch is only downloaded once and distributed to clients
- Load is removed from the GFI LanGuard server component and distributed amongst relay agents
- Since computers are managed from multiple relay agents, it increases the number of devices that can be protected simultaneously.
In a network, computers can be grouped and each group can be assigned to a relay agent. For more information refer to Configuring Relay Agents.
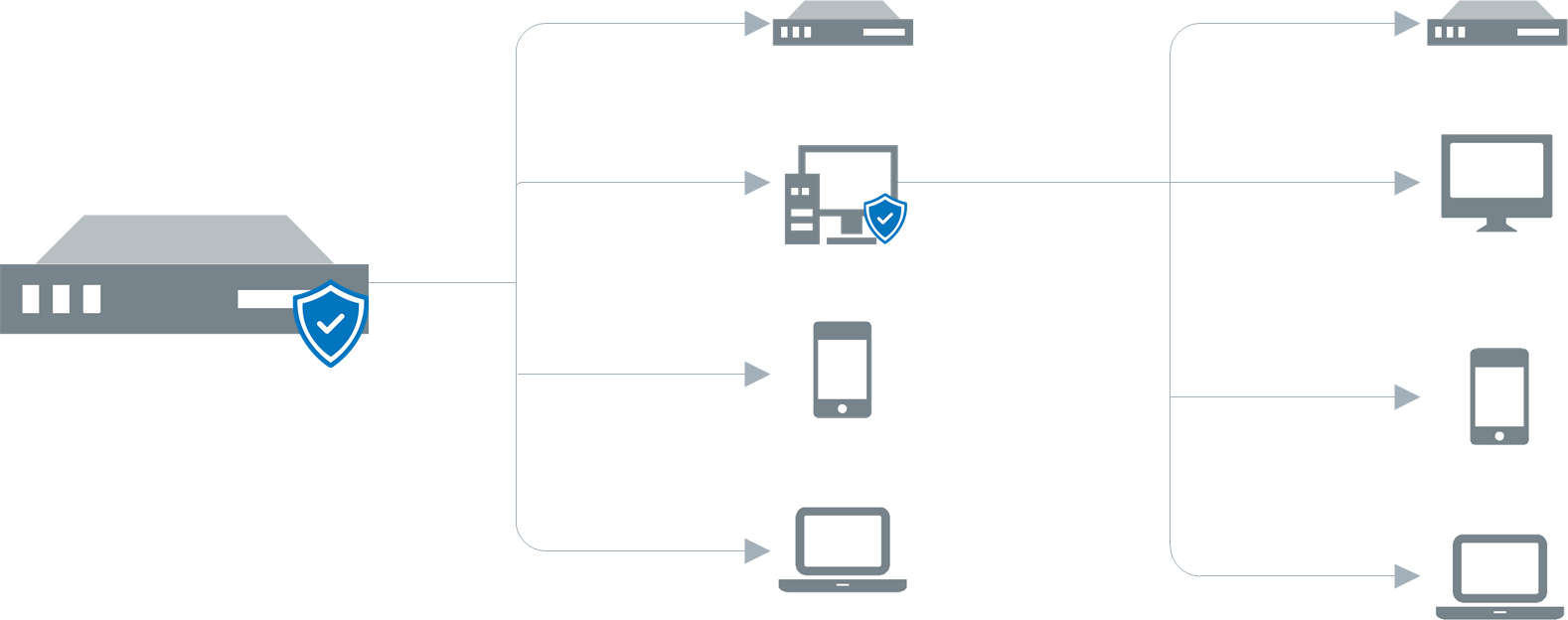
In mixed mode, GFI LanGuard is configured to work in Agent mode on some computers and in Agent-less mode on other computers or devices.
The following screenshot shows how GFI LanGuard can be deployed in mixed mode on a Local Area Network (LAN):