Overview of virtual router redundancy protocol (VRRP) with policy-based routing (PBR) and VLANs
The VRRPVirtual Router Redundancy Protocol provides automatic assignment of IPInternet protocol routers, using virtual routers as proxies for physical routers. A virtual router with a static IP address acts as a gateway between the router and the Exinda Appliances. The VRRP receives traffic requests and distributes them to the appliances connected to it, providing greater reliability and steady traffic requests distribution.
A switch can be configured to act as a VLAN to group Exinda Appliances connected to different physical switches. This out-of-path deployment decreases latency and increases performance for networks with VLANs.
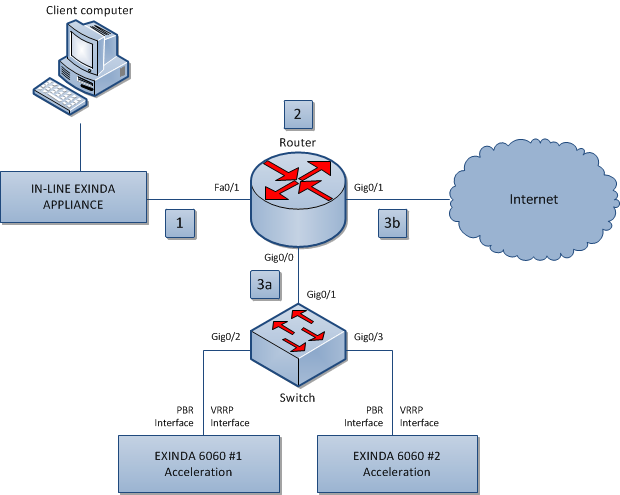
VRRP with PBR and VLANs
NOTE
All traffic between the network components in this image is bi-directional.
- The client computer requests access to a location on the Internet.
- The request is sent to the router, where the source, destination is analyzed and compared to the policy configured on the router.
- Based on the results of the analysis, the request is:
- sent to the switch, which evenly distributes the traffic between the connected Exinda appliances, and then back through the router to the requested destination.
- sent directly to the requested destination.
For more information about VRRP with PBR and VLANs, see these topics: