Overview of virtual router redundancy protocol (VRRP) with policy-based routing (PBR) and IP service levels of applications (SLA) tracking
The VRRPVirtual Router Redundancy Protocol provides automatic assignment of IPInternet protocol routers, using virtual routers as proxies for physical routers. A virtual router with a static IP address acts as a gateway between the router and the Exinda Appliances. The VRRP receives traffic requests and distributes them to the appliances connected to it, providing greater reliability and steady traffic requests distribution.
To increase fault-tolerance, configure the router to monitor SLA tracking. IP SLA configurations act as a heartbeat mechanism between the router and applicable SLA hosts.
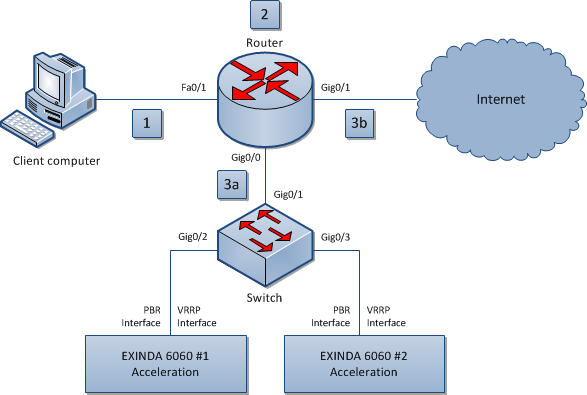
VRRP with PBR and IP SLA Tracking
NOTE
All traffic between network components in this image is bi-directional.
- The client computer requests access to a location on the Internet.
- The request is sent to the router, where the source, destination, and service levels for the requested application is analyzed and compared to the policy configured on the router.
- Based on the results of the analysis, the request is: either
- sent to the switch, which evenly distributes the traffic between the connected Exinda appliances, and then back through the router to the requested destination.
- or, sent directly to the requested destination.
Limitations
This configuration is only supported on Cisco routers and only on the following releases:
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T, 12.2(25)S, or Prior Releases
Configuration instructions can be found here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_pi/configuration/12-4t/iri-12-4t-book/iri-pbr-mult-track.pdf
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T, 12.2(33)SXH, and Later Releases
Configuration instructions can be found here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_pi/configuration/12-2sx/iri-12-2sy-book/iri-pbr-mult-track.pdf
For more information about VRRP with PBR and VLANs with IP SLA tracking, see the topics listed below: