Connect Exinda SD-WAN to broadband modems
Exinda SD-WANSoftware-Defined Wide Area Network requires connection of one or more modems, such as DSLDigital Subscriber Line, cable, or cellular broadband. Configure the modems for operation according to the ISPIntenet service provider's instructions and then configure the WANWide Area Network ports of the Exinda SD-WAN. In many cases the modems are set for DHCPDynamic Host Configuration Protocol by default, and no additional configuration is required. Some cable modems may require a power-cycle (turn off and on) to associate with a new MACMedia Access Control address after connecting to the Exinda SD-WAN.
Note that some older modem models may require a reset to associate with a new MAC address when connecting to the Exinda SD-WAN. This may further require the modems to be reconfigured with the parameters from the ISP.
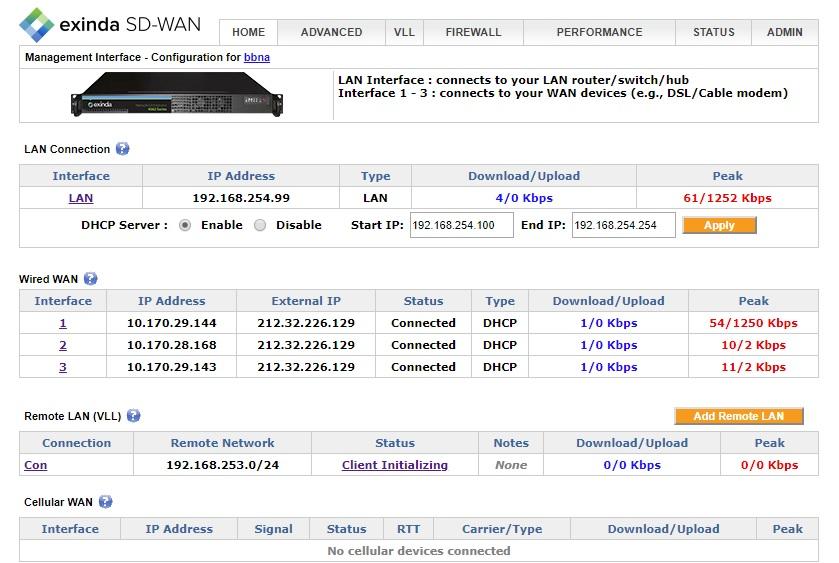
Exinda SD-WAN Management Interface
In order to connect each wireline modem, use an Ethernet cable to connect the “LANLocal area network” or “Ethernet” port of the modem and connect the other end of the cable to any wired WAN port of the Exinda SD-WAN. One of the LEDs on the connector on the Exinda SD-WAN lights up after both the modem and the Exinda SD-WAN are powered on and the modem is properly connected to the Exinda SD-WAN.
If the modems do not use DHCP, the WAN connection details need to be configured for each non-DHCP modem in the Exinda SD-WAN Management Interface, as detailed below.
Configuration of wired WAN ports
For each wired WAN port there is a corresponding status row on the Home tab. Each port is labeled with an index from 1 (WAN1) to 4 (WAN4) (or 2, 8 or 12 depending on the model) which is visible on the front panel of the Exinda SD-WAN, as well as in the left column of the tab of the Exinda SD-WAN Management Interface.
Each active wired WAN port on the Exinda SD-WAN which is connected to a modem needs to be configured with an IPInternet protocol address.
To configure a wired WAN port, click on the corresponding port index in the first column of the tab. If the wired WAN port is not in use, select Disable and click OK. Otherwise, select Enable, then specify the configuration mode for the WAN port, either DHCP, Static, PPPoEPoint-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet, or Pass Through, as appropriate.
After configuring each wired WAN port, click OK to save the corresponding WAN port settings.
Since there is probably more than one service account being used with the Exinda SD-WAN, make sure the information entered corresponds to the correct modem and port index as determined by how the modems are connected to the Exinda SD-WAN with the Ethernet cables.
Once a WAN port is configured, the IP Address column for the corresponding row is filled in automatically. The “External IP Address” is the IP address that can be used to reach the corresponding WAN port from the Internet. This address usually differs from the IP address of the WAN port when a dynamic IP address is assigned via DHCP. The Status column corresponding to the WAN port is updated, as appropriate.
For each active WAN port, the tablemenu shows the rate information on each interface for monitoring the status of each Internet connection in real time.
DHCP mode
This is the default configuration mode for each wired WAN port on the Exinda SD-WAN. Typically a DSL or cable modem has a DHCP server which is capable of assigning an IP address, called a “dynamic IP address”. In this case, the DSL or cable modem automatically configures the attached wired WAN port on the Exinda SD-WAN and no manual configuration is necessary. Optionally, alternate DNSDomain Name Server servers may be specified that override those that are provided by the modem.
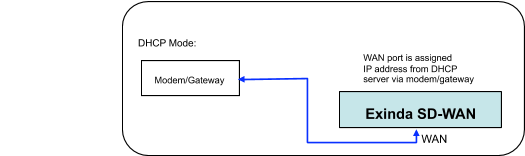
The DHCP Mode
Static IP mode
If a static IP address is assigned to a service account from the ISP, then the Static IP mode should be selected for the corresponding Exinda SD-WAN wired WAN port. The assigned static IP address needs to be entered in the User Configuration tab for the corresponding Exinda SD-WAN wired WAN port. If the ISP has assigned several static IP addresses for the same service account, one of these static IP addresses needs to be assigned to the corresponding wired WAN port on the Exinda SD-WAN.
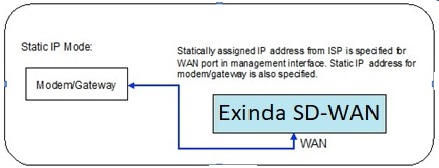
The Static IP mode
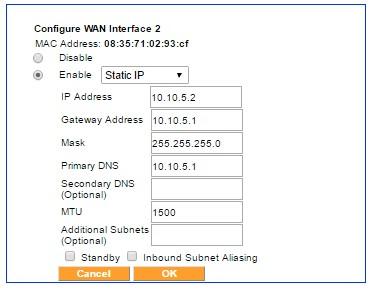
An example of Static IP configuration for WAN interface
The Gateway IP address, the Mask of the network, and Primary DNS for the service account also need to be filled in; these parameters should be provided by the ISP. You can check the Inbound Subnet Aliasing check box if required. A field for optionally entering an IP address for a secondary DNS server is also provided.
Finally, one or more IP subnets may be specified in Additional Subnets. The additional subnets should be specified in CIDRClassless Inter-Domain Routing notation (for example, 172.16.1.0/24) with comma deliminators. Normally, this field should be left blank, but if one or more additional subnets are specified, the designated WAN interface which is in Static IP mode is prepared to send and receive traffic to and from the specified subnet.
Inbound subnet aliasing
For each WAN port configured in the Static IP mode, there is an option to activate the Inbound Subnet Aliasing. If this option is enabled, the Exinda SD-WAN device acts as a proxy in the ARPAddress Resolution Protocol protocol for all IP addresses in the IP address range that are specified by the given IP address and subnet mask. This may be necessary in order for inbound traffic from the Internet to reach all of the devices in the specified subnet.
PPPoE
Some of the older DSL modems use the PPPoE protocol to configure IP addresses. If that is the case, the PPPoE mode should be selected for the corresponding Exinda SD-WAN wired WAN port. The username and password given by the ISP for the corresponding service account should be entered for the corresponding Exinda SD-WAN wired WAN port.
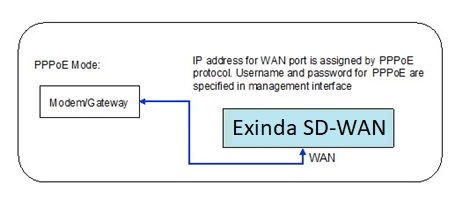
The PPPoE mode
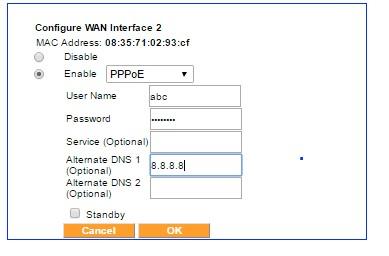
The PPPoE mode menu
If there is uncertainty as to what type of IP address configuration schemes are used by the modems, contact your ISP.
Pass Through mode
When installing the Exinda SD-WAN in an existing network with a single wired WAN backhaul connection, reconfiguration of the legacy network is not required for an Exinda SD-WAN that is configured in the Pass Through mode. This mode is available on the WAN ports. This can be useful if the legacy network is relatively complex, and the network administrator does not desire to make any configuration changes to the existing network. For example, the network administrator may wish to retain all of the existing configuration parameters of the firewall device in the legacy network.
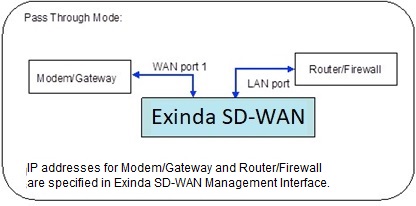
The Pass Through mode
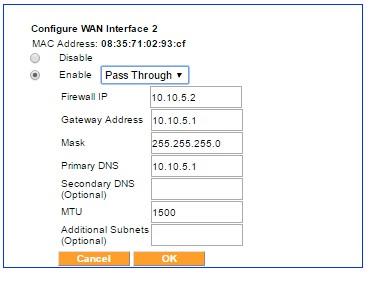
The Pass Through mode menu
In legacy networks, a gateway or modem device that provids the WAN backhaul connection is connected directly to a router/firewall device. After installation of the Exinda SD-WAN in the Pass Through mode, the Exinda SD-WAN is inserted in-line between the gateway router/modem and the router/firewall device with the gateway/modem connected to one of the WAN ports and the router/firewall connected to one of the Exinda SD-WAN LAN ports, as indicated in the illustration above. In order to configure the Pass Through mode, the Exinda SD-WAN Management Interface prompts the user to enter the IP address of the gateway/modem to be connected to that WAN port, the IP address of the firewall, the netmask of the network behind the firewall device, and the IP address of the primary DNS server. An entry for the IP address of a secondary DNS server is optional.
Note that in the Pass Through mode, WAN port 1 is not assigned an IP address. Also, it is important to note that by configuring WAN port 1 in the Pass Through mode, the Exinda SD-WAN disables its DHCP server*. The values entered on the Pass Through mode settings are exactly identical to the values for the firewall.
* As a result, when the Exinda SD-WAN is configured in Pass Through mode, it may be necessary to manually assign a static IP address to the PC which is used to access the Exinda SD-WAN Management Interface, if there is no active DHCP server to assign it a dynamic IP address.
Standby mode
Each enabled WAN port can be put in the Standby mode if desired. In this mode, a WAN port is not normally used unless no other WAN connectivity is available. This mode should be used if it is desired to use the WAN resource only as a backup in case of failure of the primary WAN connections. In order to put a WAN port in the Standby mode, select the displayed check box.
Using a Cellular Mobile Data Card
The Exinda SD-WAN has two USBUniversal Serial Bus ports which may be used as WAN interfaces for connecting to a cellular data modem. Please contact Support for the list of supported air cards.
In order to use your data card, first configure it with your personal computer using the instructions from your mobile wireless service provider. Once the card is configured, you can use it with your Exinda SD-WAN. To do this, plug your wireless data card into the Exinda SD-WAN after it has booted up. After a few seconds, the Exinda SD-WAN Management Interface includes the status for Cellular WAN interface or interfaces in the table displayed at the bottom of the Home tab.
In order to configure the cellular WAN interface, on the home page of the Exinda SD-WAN Management Interface, click the mouse on the interface index on the left side of the Cellular WAN connection table. A menu is displayed for configuring the corresponding interface as CDMACode Division Multiple Access or HSPAHigh Speed Packet Access/GSMGlobal System for Mobile Communications and for optionally setting the interface into standby mode. The Carrier and, depending on the mode, APNAccess Point Network may need to be entered. The Username and Password may also be required for configuring the interface.
When the cellular WAN interface is in the Standby mode, it is only used when all other WAN interfaces are in the inactive state. This is useful if the cellular WAN interface is used for a service provider that charges a fee that depends on data usage. When at least one of the other interfaces enters the active state, the cellular WAN interface is not used while it is in the Standby mode. When the cellular WAN interface is not in the Standby mode, the Exinda SD-WAN uses the cellular WAN interface as much as possible in order to improve performance.