Configuring IP address translation
Network Address Translation (NATNetwork address translation - A method that remaps IP addresses by changing network address information.) is a term used for the exchange of a private IP address in a packet going out from the local network to the Internet with the IP addressAn identifier assigned to devices connected to a TCP/IP network. of the Internet interface of the Kerio Control host. This technology is used to connect local private networks to the Internet by a single public IP address.
Configuring IP address translation
- In the administraton interface, go to Traffic Rules. IP address translation must be configured for the particular rules.
- Double-click Translation in the selected rule.
- In the Traffic Rule - Translation dialog, you can configure the following:
Source IP address translation (NAT — Internet connection sharing)
Source address translation is used in traffic rules applied to traffic from the local private network to the Internet. In other rules (traffic between the local network and the firewall, between the firewall and the Internet, etc.), NAT is unnecessary.
For source address translation, check Enable source NAT and select:
| Source NAT Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Default setting (recommended) |
By default, in packets sent from the LANLocal area network - A network that connects computers and other devices in a small area. to the Internet the source IP address will be replaced by IP address of the Internet interface of the firewall through which the packet is sent. This IP address translation method is useful in the general rule for access from the LAN to the Internet, because it works correctly in any Internet connection configuration and for any status of individual links. For a single leased link, or connection failover, the following options have no effect on Kerio Control's functionality. If Kerio Control works in the mode of network traffic load balancing, you can select:
HINT For maximal efficiency of the connection's capacity, go to the Configuring policy routing article. |
| Use specific outgoing interface |
Packets will be sent to the Internet via this specific link. This allows definition of rules for forwarding specific traffic through a selected Interface — so called policy routing. If the selected Internet link fails, Internet will be unavailable for all services, clients, etc. specified by this rule. To prevent from such situations, check Allow using of a different interface if this one becomes unavailable. |
| Use specific IP address |
An IP address for NAT will be used as the source IP address for all packets sent from the LAN to the Internet.
|
Full cone NAT
The typical behavior of NAT allows returning traffic only from a specific IP Address. The behavior can be adjusted to allow returning traffic from any IP Address. This is called full cone NAT.
If this option is off, Kerio Control performs so called port restricted cone NAT. In outgoing packets transferred from the local network to the Internet, Kerio Control replaces the source IP address of the interface with the public address of the firewall (see above). If possible, the original source port is kept; otherwise, another free source port is assigned. For returning traffic, the firewall allows only packets arriving from the same IP address and port to which the outgoing packet was sent. This translation method guarantees high security — the firewall will not let in any packet which is not a response to the sent request.
However, many applications (especially applications working with multimedia, Voice over IP technologies, etc.) use another traffic method where other clients can (with direct connection established) connect to a port opened by an outgoing packet. Therefore, Kerio Control supports also the full cone NAT mode where the described restrictions are not applied for incoming packets. The port then lets in incoming packets with any source IP address and port. This translation method may be necessary to enable full functionality of certain applications.
NOTE
Full cone NAT may introduce certain security threats — the port opened by the outgoing connection can be accessed without any restrictions being applied. For this reason, it is recommended to enable full cone NAT only for a specific service (i.e. to create a special rule for this purpose).
Destination NAT (port mapping):
Destination address translation (also called port mapping) is used to allow access to services hosted in private local networks behind the firewall.
For port mapping:
- Check Enable destination NAT.
- In field Translate to the following host, type a host address or DNSDomain Name System - A database enables the translation of hostnames to IP addresses and provides other domain related information. name. IP address that will substitute the packet's destination address. This address also represents the address/name of the host on which the service is actually running.
- If you want to change a port, check Translate port as well and type the port of a service. During the process of IP translation you can also substitute the port of the appropriate service. This means that the service can run at a port that is different from the port where it is available from the Internet.
NOTE
This option cannot be used if multiple services or ports are defined in the Service entry within the appropriate traffic rule.
For more information refer to Configuring traffic rules.
A default NAT rule description
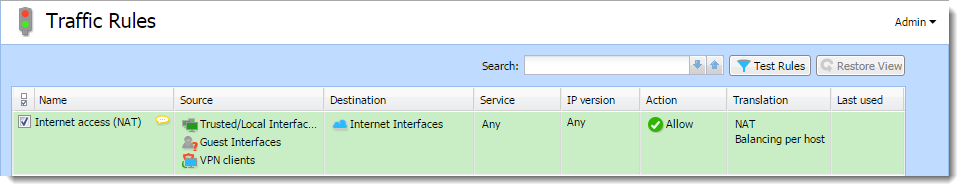
A typical traffic rule for NAT (Internet connection sharing)
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Source |
Group Trusted/Local Interfaces (from the Interfaces section). This group includes all segments of the LAN connected directly to the firewall. If access to the Internet from some segments is supposed to be blocked, the most suitable group to file the interface into is Other interfaces. Interfaces are described in the Configuring network interfaces article. If the local network consists of cascaded segments (i.e. it includes other routers), it is not necessary to customize the rule in accordance with this fact — it is just necessary to set routing correctly. For more information refer to Configuring a routing table in Kerio Control. |
| Destination |
The Internet Interfaces group. With this group, the rule is usable for any type of Internet connection. |
| Service |
This entry can be used to define global limitations for Internet access. If particular services are defined for NAT, only these services will be used for the NAT and other Internet services will not be available from the local network. |
| Actions |
The Action must be set to Allow. |
| Translation |
In the Source NAT section select the Default settings option (the primary IP address of the outgoing interface will be used for NAT). The default option will ensure that the correct IP address and Interface are used for the intended destination. WARNING Destination NAT should not be configured for outgoing rules, except under very unique circumstances. |
| Placing the rule |
The rule for destination address translation must be preceded by all rules which deny access to the Internet from the local network. |
Such a rule allows access to the Internet from any host in the local network, not from the firewall itself (i.e. from the Kerio Control host).
Traffic between the firewall and the Internet is enabled by a special rule by default. Since the Kerio Control host can access the Internet directly, it is not necessary to use NAT.

Rule for traffic between the firewall and hosts in the Internet