Configuring Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
Demilitarized zone (DMZDemilitarized zone - A security method that separates internal LAN networks from external networks.) is a special segment of the local network reserved for servers accessible from the Internet. It is not allowed to access the local network from this segment — if a server in the DMZ is attacked, it is impossible for the attacker to reach other servers and computers located in the local network.
Configuring DMZ
As an example we will suppose rules for a web server located in the
DMZ. The demilitarized zone is connected to the DMZ interface included in group Other Interfaces. The DMZ uses subnet 192.168.2.x, the web server's IP addressAn identifier assigned to devices connected to a TCP/IP network. is 192.168.2.2.
Now you will add the following rules:
- Make the web server accessible from the Internet — mapping HTTPHypertext Transfer Protocol - protocol for exchange of hypertext documents in HTML. service on the server in the DMZ,
- Allow access from the DMZ to the Internet via NATNetwork address translation - A method that remaps IP addresses by changing network address information. (IP address translation) — necessary for correct functionality of the mapped service,
- Allo access from the LANLocal area network - A network that connects computers and other devices in a small area. to the DMZ — this makes the web server accessible to local users,
- Disable access from the DMZ to the LAN — protection against network intrusions from the DMZ. This is globally solved by a default rule blocking any other traffic (here we have added the blocking rule for better understanding).
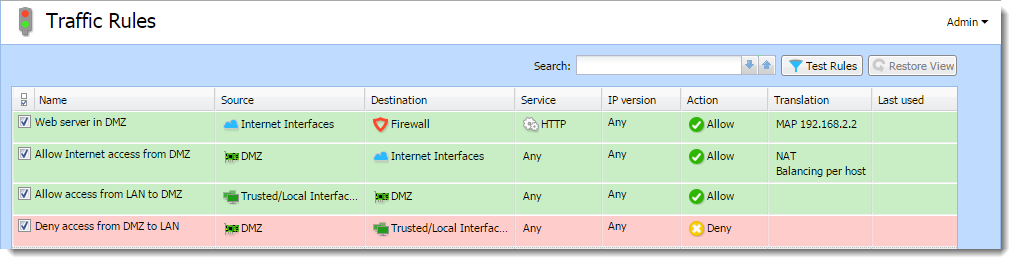
Traffic rules for the DMZ
Hint
To make multiple servers accessible in the DMZ, it is possible to use multiple public IP addresses on the firewall's Internet interface — so called multihoming.